Women’s Imaging

Susan L. Summerton, M.D.


Women’s Imaging
•Breast imaging
•Imaging modalities
•Evaluation of common problems
•Pelvic imaging
•Pelvic pain
•Ectopic Pregnancy
•Adnexal Torsion


Imaging modalities commonlyused in breast imaging
•Mammography
•Digital mammography
•Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD)
•Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
•US
•MRI


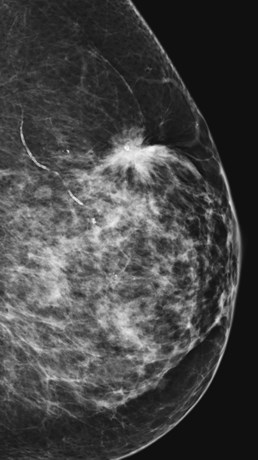
Digital Mammography
•Electronic image ofthe breast
•Stored directly ina computer
•Can manipulate imagesto increase contrast


Advantages ofDigital Mammography over Films
•Easier access to images & computer aideddiagnosis
•Can transmit images electronically
•Lower average dose of radiation withoutcompromise in diagnostic accuracy
•Images can not be damaged (like film)
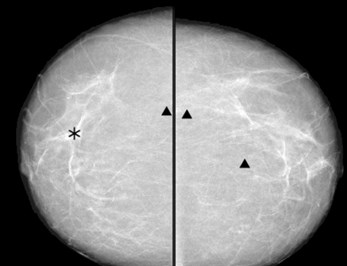
•Computer Aided Diagnosis
•Major Disadvantage: $$$$

COMPUTERAIDEDDIAGNOSIS


Her workup should include which of thefollowing (select all that apply):
Case #1, 35 yo woman with a palpable lumpin her left breast..
a.Bilateral mammogram
b.Left mammogram only
c.Left breast ultrasound
d.Possible ultrasound,depending on whatmammogram shows
Let the American College of Radiology’sAppropriateness Criteria help you…

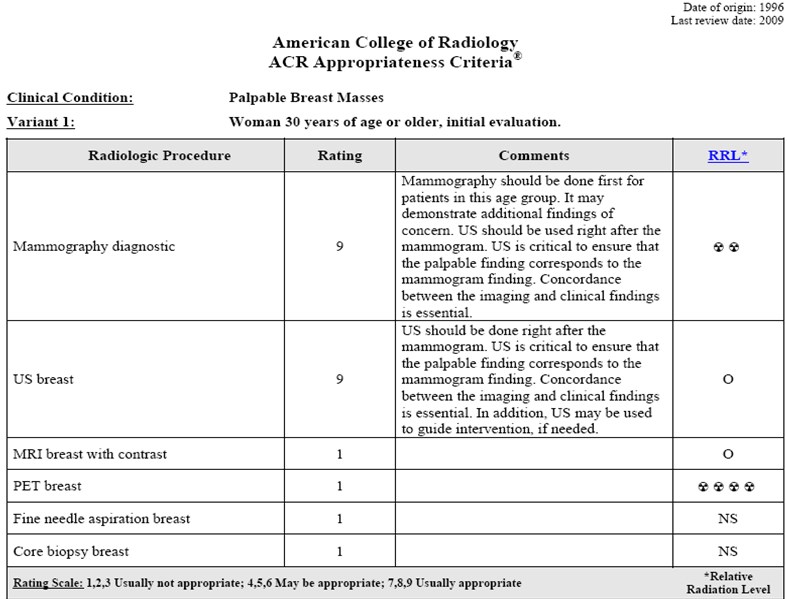

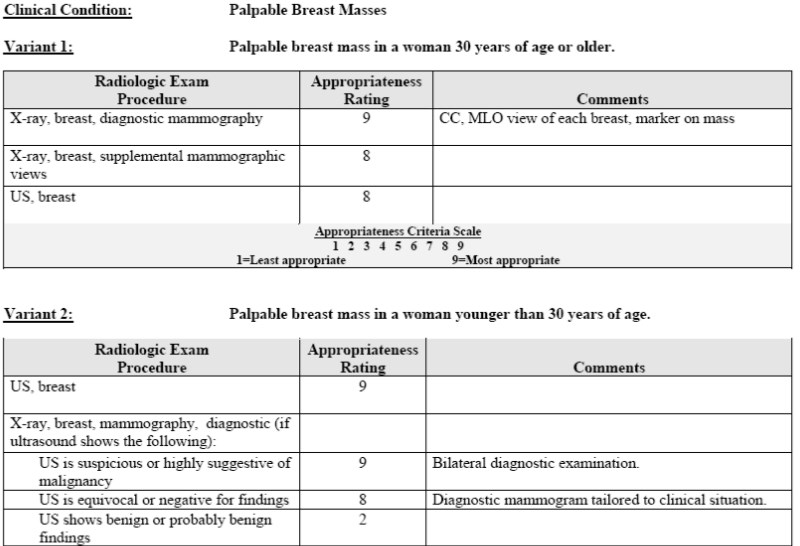
Reprinted with permission of the American College of Radiology. No other representation of this material is authorized withoutexpress, written permission from the American College of Radiology. Refer to the ACR website at www.acr.org/ac of the most currentand complete version of the ACR Appropriateness Criteria®.

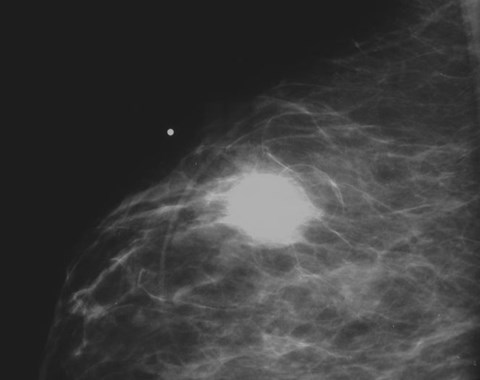
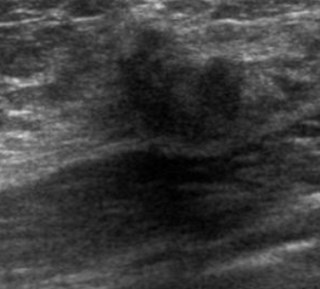
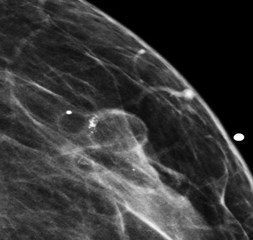
45 yo woman with a palpable lump
Mammogram showsspiculated mass
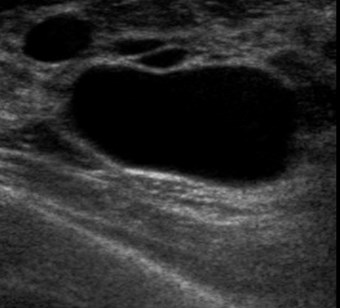
US: Solid mass with
malignant features

US features of benign masses
Homogeneous internal echoes
Smooth margin, echogenic rim(white line visible around mass)
Enhanced sound transmission
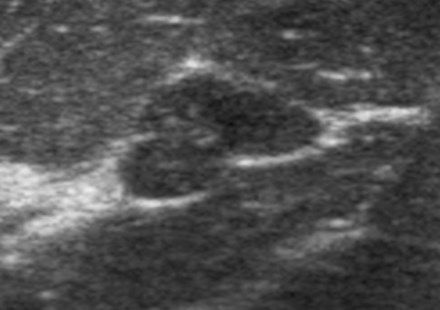
CYST
FIBROADENOMA

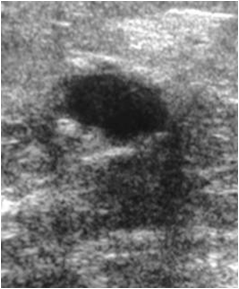
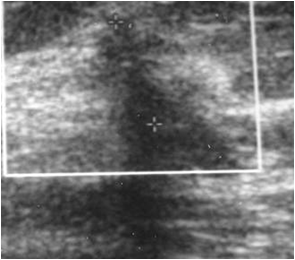
US Features of Malignancy
Hypoechoic (darker than fat)
Irregular, spiculated margins
Posterior acoustic shadowing


mass
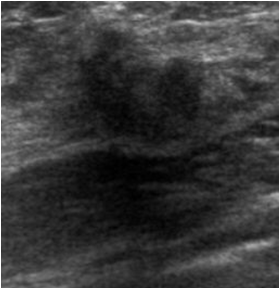

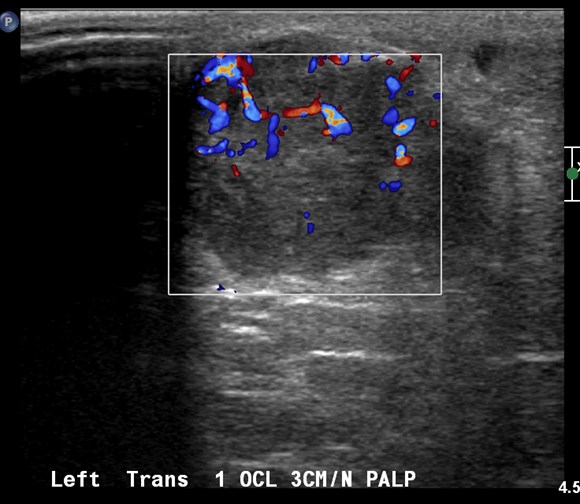
65 yo woman, history of lumpectomy,presents with new lump

25 yo with palpable left breast lump
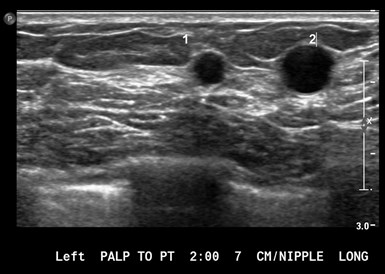
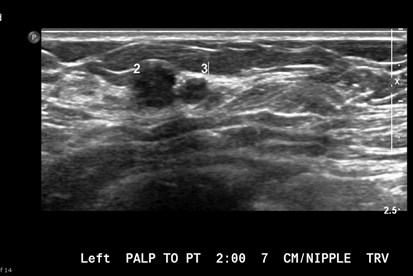

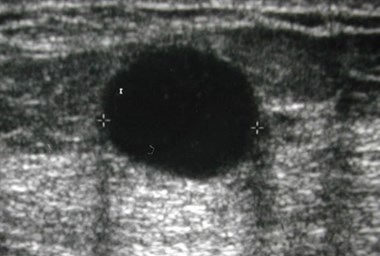
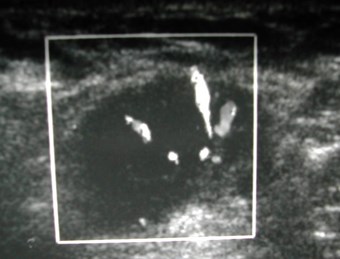
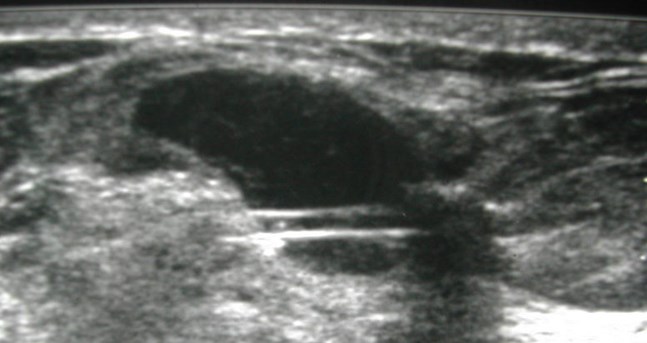


Ultrasound
•Important adjunct to mammography
•Primary imaging modality in < 30 yo withbreast problem
•Limitations
•Limited visualization of calcifications
•Most incidental findings benign
•Operator dependant
•Time consuming


Current ACR Practice Guidelinesfor breast US examination (2011)
•Identify & characterize palpable and nonpalpableabnormalities: further evaluation of clinical &mammographic findings
•Guidance for interventional procedures
•Evaluation of problems with implants
•Treatment planning for radiation


Current ACR Practice Guidelinesfor breast US examination (2011)
•Supplement to mammography, screening foroccult cancers in certain populations of women(dense fibroglandular breasts who are also atelevated risk of breast cancer or with newlysuspected breast cancer) who are not candidatesfor MRI or have no easy access to MRI
•(newly added to ACR guidelines in 2011)


breast pain…tenderness…burning…discomfort…tingling….
How do we image patientswho present with….How do we image patientswho present with….
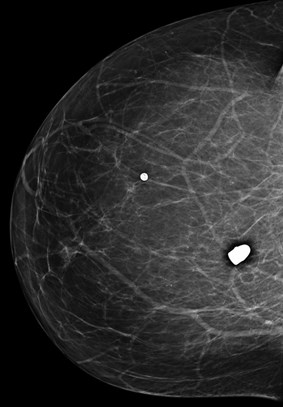

The first question we always ask….Are the symptoms focal or diffuse?
•If diffuse and bilateral no imagingnecessary (this is normal!)
•History is important, may help determineetiology of pain
•? Recent car accident, other blunt trauma
•? New meds (hormones)
•If focal US helpful (????)


The Value of Ultrasound in theEvaluation of Breast Pain
Debra Copit MD, Julia Peoples MD, David Lee MD, AEMC Phila, PA
•Breast Pain: Most common breast symptom forwhich women seek medical attention
•Rare presenting symptom of breast cancer
•Cancer Prevalence: 0.4 - 3.2%
•ACR practice guideline for performance of breastultrasound
“Evaluation and characterization of palpablemasses and other breast related signs and/orsymptoms”



Study details and results
•Retrospective review
•Focal or diffuse breast pain without palpable abnormality
•257 areas of pain in 209 patients
•Study result:
•Ultrasound usually normal
•Small % of patients had US findings: cysts
•No cancers diagnosed
•Conclusion:
•Pain + normal mammogram ≠ US
•Patients may be better served with reassuranceand clinical management


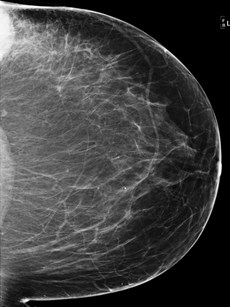
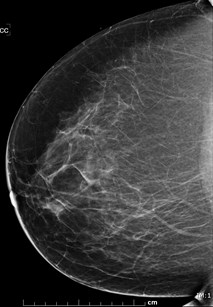
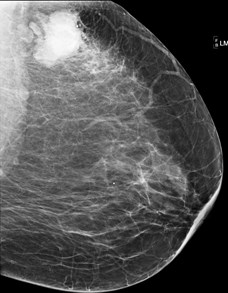
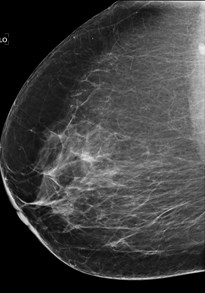
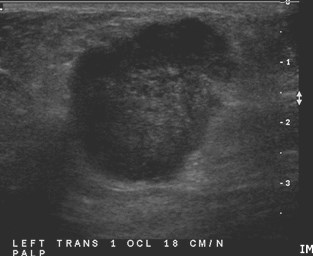
35 yo woman:palpable left
breast mass

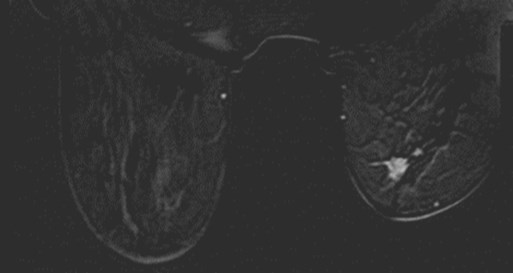
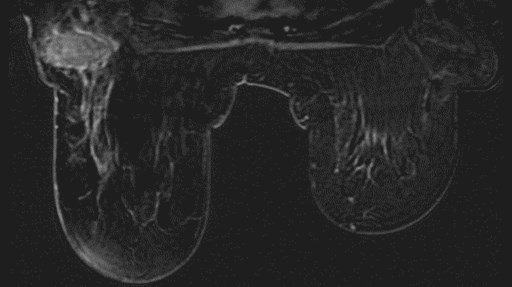

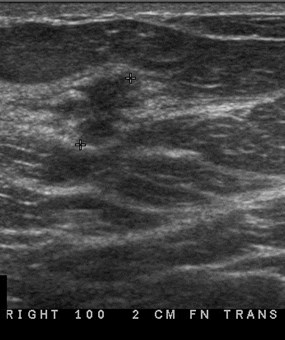
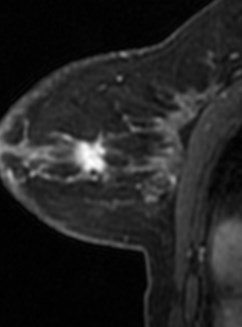
MRI ordered for staging


MRI in Breast Imaging:Indications
•Staging newly diagnosed cancer
•Screening (high-risk, dense breasts)
•Assess residual disease(neoadjuvant chemo)
•Positive axillary nodes ofunknown primary


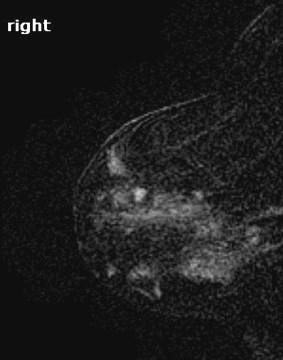
MRI in Breast Imaging
•High Sensitivity (98-100%)
•Requires IV contrast
•Gadolinium
•Limitations:
•Low Specificity (37-97%)
•Lengthy examination
•Expensive


MRI for staging breast cancer
•More accurate than mammography and US
•MR-only detected multifocal-multicentric
•20-30%
•Clinical uses
•Newly diagnosed breast cancer
•Size
•Post surgery with + margins
•Management change – mastectomy
•NOT indicated for workup of palpable lump


Potential Applications:Suspected Carcinoma
•Several studies have suggested that anegative MRI virtually excludes invasivecancer
•But, a negative MRI should NOT precludebiopsy of a suspicious mammographic orsonographic finding


MRI in high risk patients:Breast cancer risk assessment
•# of first degree relatives with breast Ca
•Personal history of breast cancer, DCISor LCIS
•Age of menarche (increases withearlier)
•Age gave birth to 1st child (increaseswith older age at first term live birth)
•Patient’s Age (increased with age)
•Race (White > Black)
http://www.cancer.gov/bcrisktool/


American Cancer SocietyBreast MRI Screening Guidelines: High Risk
•20-25% lifetime risk for breast ca
•Known BRCA 1 or 2 mutation carriers
•Untested first degree relatives of proven carriers
•Radiation to chest between ages 10 - 30
•Certain rare genetic syndromes
•Li Fraumeri, Cowden, Peutz Jegher, Ataxia-telangiectasia


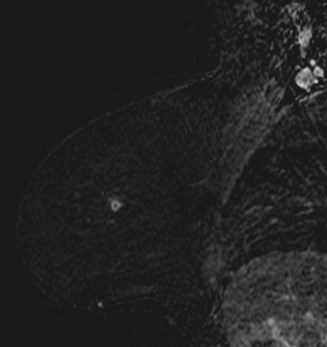
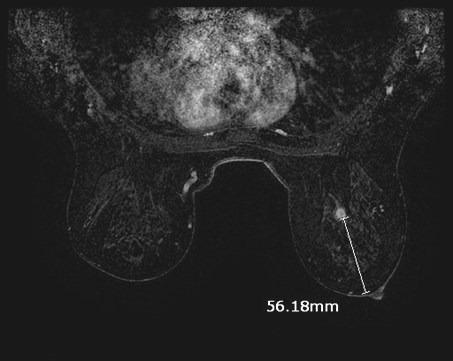
Screening MRI on 46 year old:BRCA1 positive
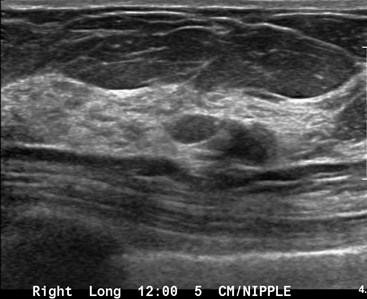


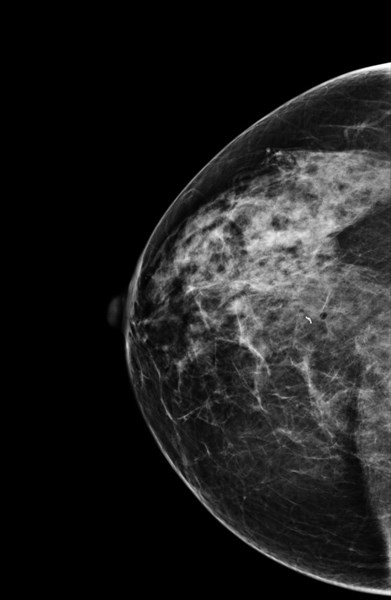
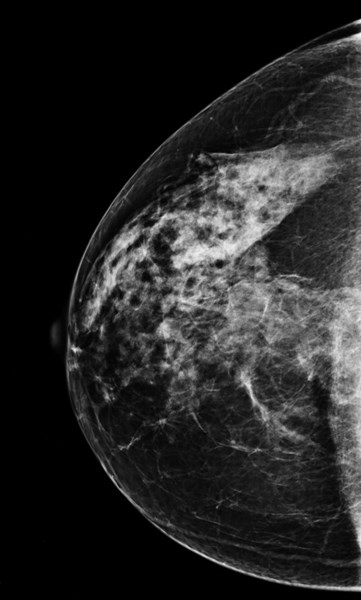
RCC pre bx
RCC post bx


What About Intermediate Risk?
•15%-20% lifetime risk:
•Personal history of breast cancer
•Biopsy that showed atypia or LCIS
•Dense breasts
•Insufficient evidence to recommend foror against screening with MRI


Breast MRI
•NOT meant to replace mammography
•MRI screening can detect otherwise occultcancer but it has not yet been shown todecrease mortality, i.e., life expectancy frombreast cancer


(Future) Developments in BreastImaging Technology
•Mammography-based
•Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT)
•Dedicated Breast CT
•Ultrasound
•Whole Breast US
•Nuclear Medicine
- PEM (Positron Emission Mammography): dedicatedbreast PET with CT - does not require compression!
- Breast Specific Gamma Imaging (BSGI)


Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
•Images acquired at different angles
•X-ray detector sweeps around stationary(compressed) breast
•Allows 3-D reconstruction
•Can scroll through images
•Similar to CT



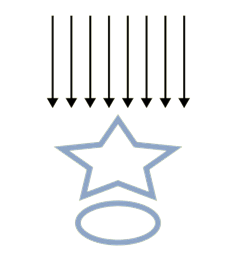
Conventional (2-D) Mammogram
X-rays
2 objects being imaged
2-D image
Objects overlap on final image



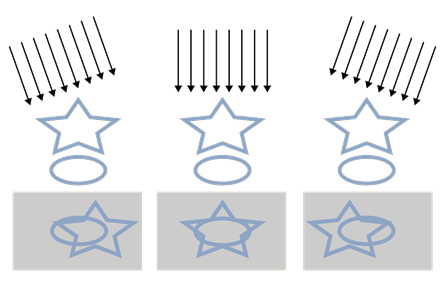
Tomosynthesis Acquisition
X-rays
2-D raw data images
Image from multiple angles
Exposure #1 Exposure #6 Exposure #11


Digital Breast Tomosynthesis:Advantages
• patient discomfort and compression
• lesion detection in non fatty breasts
•Reduces tissue overlap
•Reduces callback rate
•Potential advantages
•Imaging in a single compression
•Improved cancer detection in dense breast tissue
•Reduced number of negative biopsies


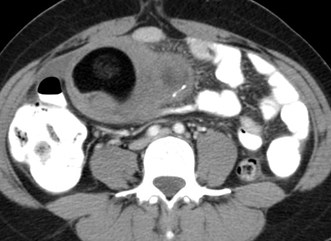
Acute Pelvic Pain
•Pain < 3 months duration
•Common cause of hospital and out-patientvisits
•Women 20-40’s surgical misdiagnosis rate30-40%
•Imaging plays a very important role in clinicalmanagement


Women with pelvic pain:First question to ask…
•If the patient is of menstrual age
•Could you be pregnant????
•Negative pregnancy test
•Gyn etiology
•Non-gyn etiology
•Positive pregnancy test
•Obstetric
•Non-obstetric etiology
•ULTRASOUND IS FIRSTSTUDY OF CHOICE
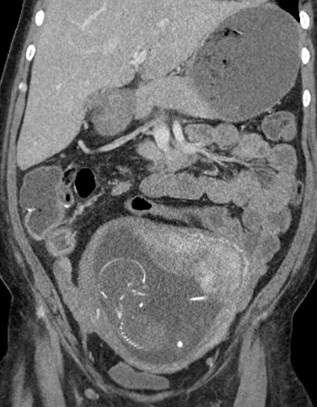


What if ultrasound isnondiagnostic?
•CT useful (If patient is not pregnant)
•Suspected abscess or hematoma, PID,postpartum complications, bowel disease
•MRI useful
•For acute gynecologic disease and/orif pregnant
•Hemorrhagic cysts, endometriosis,ovarian torsion, dermoid cysts,degenerating fibroids


Differential diagnoses foracute pelvic pain
•Gynecologic (US)
Adnexal Torsion
Ectopic pregnancy
Ruptured ovarian cyst
Endometriosis
PID
•Non-gynecologic (CT)
Urolithiasis
Appendicitis
Diverticulitis
Bowel perforation



Ectopic pregnancy
•Symptoms:
•Classic clinical triad: < 20% of the time
•Abdominal pain
•Bleeding
•Adnexal mass
•Symptoms may be vague, non-specific
•May present with hypotensive shock


Which of the following would place her atincreased risk for ectopic pregnancy?(select all that apply)
Case #2: 25 yo pregnant female presents withpelvic pain.
a.Prior ectopic
b.History of PID
c.History of uterine arteryembolization
d.IVF
e.History of tubal surgery


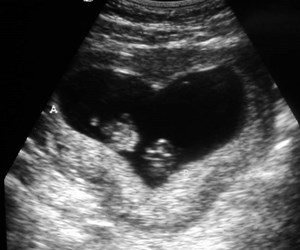
Ectopic Pregnancy
•1-2% of all pregnancies
•Lead cause of maternal mortality in1st trimester
•Diagnosis depends on combination of..
•US findings/HCG
•Risk factors
•Prior ectopic
•History of PID
•IUD with pregnancy
•IVF
•History of tubal surgery
Consider in any female of reproductive age with acute pelvic pain


Location of ectopic pregnancy
•Fallopian tube
•Ampullary - isthmic - 95%
•Interstitial (cornual) - 2 - 3%
•Extra-tubal: rare
•Abdominal, cervical, ovarian
•Sonographic Evaluation
•Transabdominal First:
•Look for large massand/or blood
•Transvaginal Second
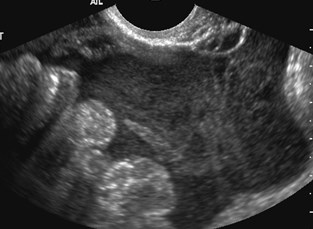
BLOOD
BOWEL
Normal Tube

If IUP detected with EVUS:Risk of ectopic is ~0%
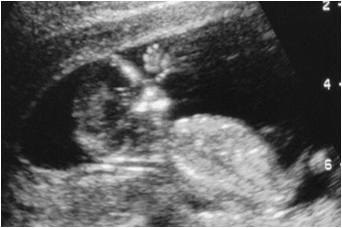
If No IUP detected with EVUS(and HCG > 3000 - 3rd Intl standard)
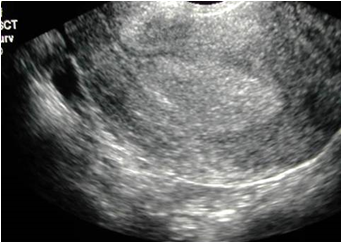
Risk of ectopic very high


US findings in ectopic
•Most specific sign-minority
•Visible extrauterine embryo
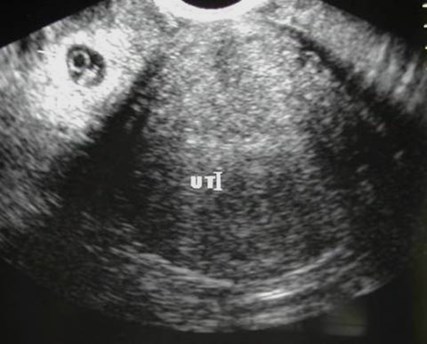
UTERUS


More common signs of ectopic
•Free simple or complex fluid
•Echogenic tubal rings
•Adnexal mass
•Hematosalpinx
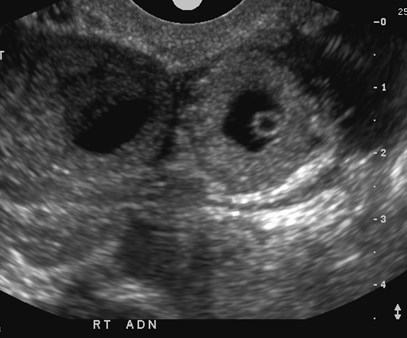

uterus
BLOOD IN CDS

BOWEL

HEMOPERITONEUM
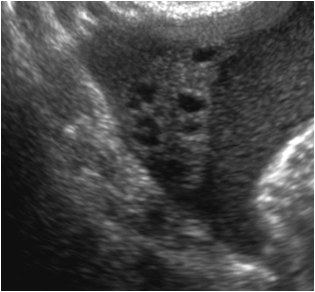
RIGHT OVARY
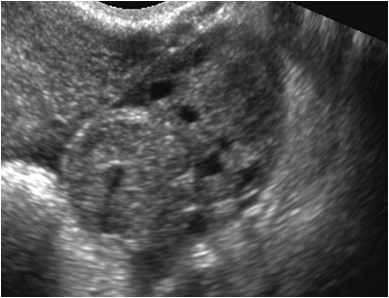
LEFT OVARY




Potential Pitfalls:Pseudosac
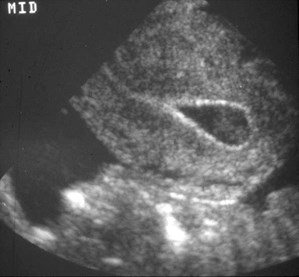
•Present in 5-10% of ectopic pregnancies
•Fluid located in center of endometrial canal
•Usually oval in shape
•Can mimic IUP
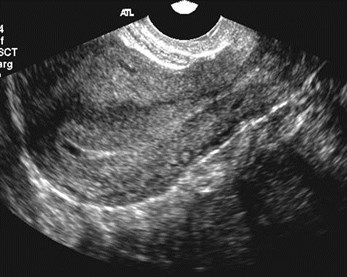


Corpus Luteum Cyst vsEctopic Pregnancy
•Corpus luteal cyst
•Eccentric with rim of ovarian tissue
•Corpus luteal cyst is equal to or lessechogenic
•Tubal ring
•Concentric echogenic rim
•Often surrounded by a hematosalpinx
•Echogenicity of tubal ring greater thanovary
•When corpus luteum visualized, 80% had ipsilateral ectopicpregnancy
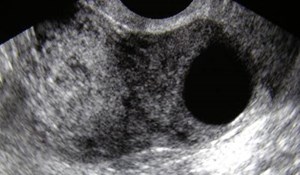
CL
TR

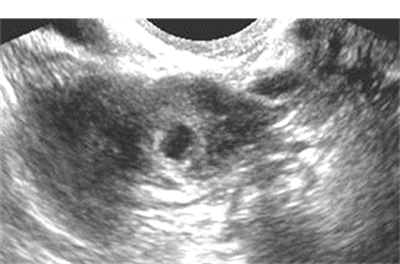
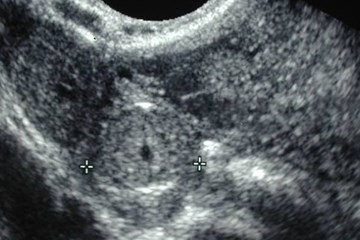
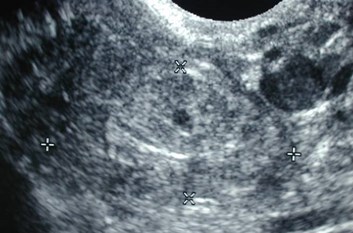
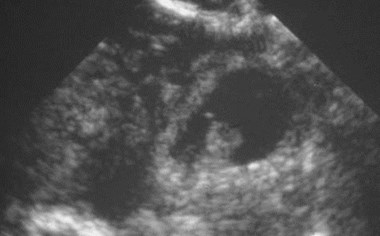
Ectopic pregnancies:echogenic tubal rings

Corpus Luteal Cysts
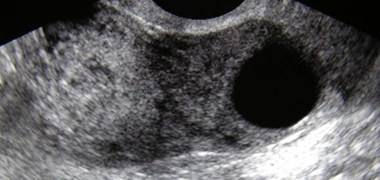
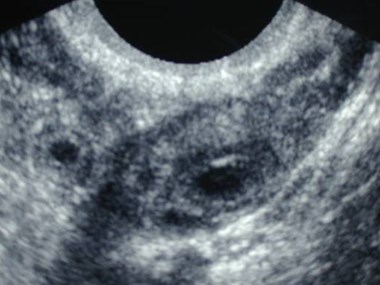
CL
CL
ectopic
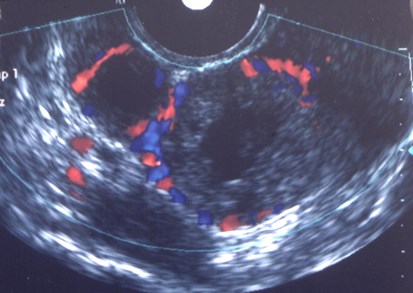
ectopic
CL

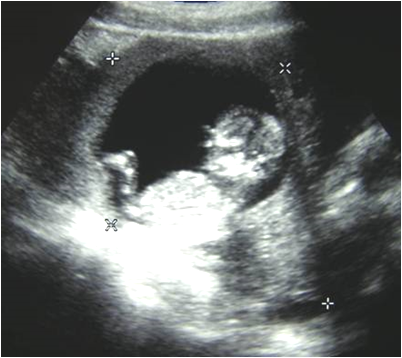
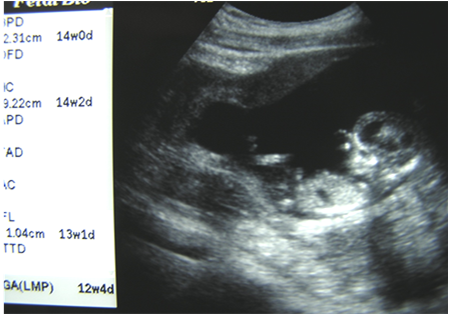
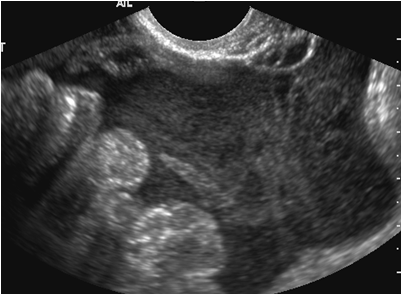
Intraabdominalpregnancy
30 yo pregnant woman


Case #3: 45 yo nonpregnant female with acuteleft pelvic pain. Ovarian torsion should beconsidered if…(select all that apply)
Audience Question
a.History of prior pelvic surgery
b.History of known left ovariandermoid
c.Ovary is normal in size onultrasound, but contains acomplex cyst
d.Ovary is enlarged (> 5 cm)and edematous, regardless ofcolor Doppler findings


Ovarian Torsion
•Acute onset of pain
•+/- Nausea & Vomiting
•> 50% have had similar prior episodes
•Doppler Ultrasound is initial study of choice


Adnexal/Ovarian torsion
•In children/young adults: idiopathic
•In older adults: benign ovarian mass
•Risk factors
•Prior pelvic surgery
•Ovarian cysts
•Pregnancy
•No risk factors in~50%


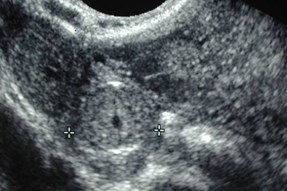
Ultrasound findings in torsion
•Enlarged edematous ovary (> 5 cm)
•Intraovarian mass (> 4 cm)
•Complex > cystic > solid
•Complex adnexal mass, fluid levels
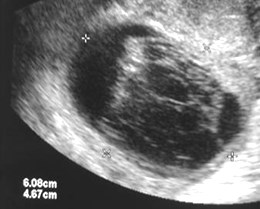
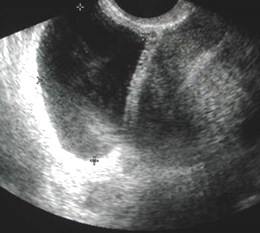
FLUID
OVARY


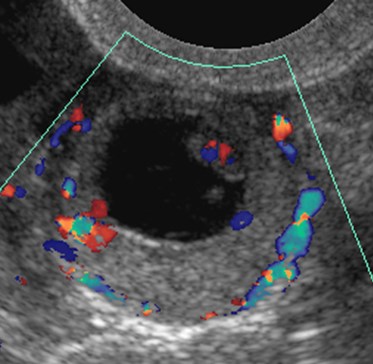
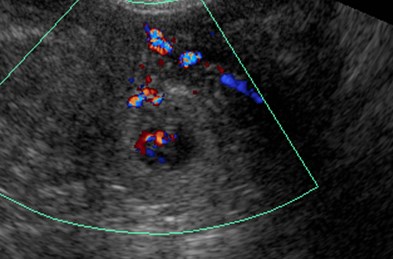
Color Doppler US in Torsion
•Color Doppler findings of torsion variable
•degree of twist
•degree of vascular compromise
•Blood flow may be present even when ovary torsed
•Dual arterial supply of ovary
•Ovarian artery
•Branches of uterine artery
•Color Doppler flow predicts outcome
•When absent ovary not viable
•When present ovary usually viable

CT findings of torsion
•Enlarged ovary, high in pelvis, anterior to uterus
•Deviated uterus to side
•Lack of enhancement
•Engorged adnexal vessels
•Ascites
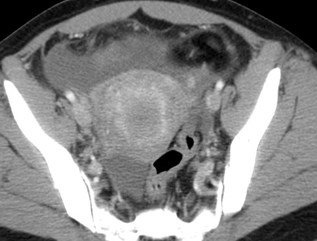


Questions from theAudience?


Regarding ectopic pregnancy, which one ofthe following statements is TRUE?
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.A pseudosac is another name for a corpusluteal cyst that mimics an ectopic pregnancy
b.The most common location is in the ampullaryportion of the fallopian tube
c.hCG level> 1500 & no visible intrauterinepregnancy risk of ectopic is very high
d.An echogenic tubal ring is the most specificsign of an ectopic pregnancy.


Regarding ectopic pregnancy, which one ofthe following statements is TRUE?
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.A pseudosac is another name for a corpusluteal cyst that mimics an ectopic pregnancy
b.The most common location is in the ampullaryportion of the fallopian tube
c.hCG level> 1500 & no visible intrauterinepregnancy risk of ectopic is very high
d.An echogenic tubal ring is the most specificsign of an ectopic pregnancy.


Regarding ectopic pregnancy, which one of thefollowing statements is TRUE?
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.A pseudosac is another name for a corpus lutealcyst that mimics an ectopic pregnancy
b.The most common location is in the ampullaryportion of the fallopian tube
c.hCG level> 1500 & no visible intrauterinepregnancy risk of ectopic is very high
d.An echogenic tubal ring is the most specific sign ofan ectopic pregnancy.
K


Imaging modalities that are indicated forbreast cancer screening include:
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.Mammography
b.Mammography and US (in certainpatients)
c.Mammography and MRI (in certainpatients)
d.Mammography, US and MRI (in certainpatients


Which of the following is an advantage ofdigital breast tomosynthesis?
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.Characterizes calcifications better thantraditional mammography
b.Can diagnose cysts without the need forultrasound
c.Decreased radiation dose compared totraditional mammography
d.Decreased recall rate for screeningmammograms
K


Breast MRI: Which of the following statements istrue?
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.Breast MRI requires IV contrast(Gadolinium)
b.When used as screening study, itreduces mortality from breast cancer
c.Indicated in patients at intermediate riskfor breast cancer
d.Should be obtained in patients who havebiopsy proven LCIS and/or atypia


Breast MRI: Which of the following statements istrue?
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.Breast MRI requires IV contrast(Gadolinium)
b.When used as screening study, itreduces mortality from breast cancer
c.Indicated in patients at intermediate riskfor breast cancer
d.Should be obtained in patients who havebiopsy proven LCIS and/or atypia


Breast MRI: Which of the following statements istrue?
Women’s ImagingSusan L. Summerton, M.D.
a.Breast MRI requires IV contrast(Gadolinium)
b.When used as screening study, it reducesmortality from breast cancer
c.Indicated in patients at intermediate risk forbreast cancer
d.Should be obtained in patients who havebiopsy proven LCIS and/or atypia
K

References
1. Combined screening with ultrasound and mammography vsmammography alone in women at elevated risk of breast cancer.Berg WA, Blume JD, Cormack JB, et al. JAMA 2008;299:2151-2163
2. Pelvic pain: overlooked and underdiagnosed gynecologic conditions.Kuligowska E, Deeds L, Kang L. RadioGraphics 25:3 – 20, 2005
3. Diagnostic Criteria for Nonviable Pregnancy Early in the FirstTrimester, PM Doubilet, CB Benson, T Bourne, et al. NEJM October2013- 369: 15, 1443-1451.
4.Evaluation of Palpable Breast Masses, Klein S, AAFP, 2005May;71(9).1731-1738
5.Negative Predictive Value of Sonography and Mammography inPatients with Focal Breast Pain. Tumyan et al, The Breast Journal2005;333-337
6.Multidetector CT of the female pelvis. Siddall KA, Rubens DJ; RadiolClin N Am 43:1097 – 1118, 2005